5. What Command Do You Use to Determine Whether You Can Reach Another Computer on the Local Network?
The ping utility is a basic, yet the most widely used network command-line tool used to test network connectivity and name resolution of a remote device. The device can be some other computer, network switch, or a router on your local network. Or, it can exist a device on the Internet, such equally a spider web server, web site, DNS server, or email server. Ping uses the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Repeat function as described in RFC 792. A minor data bundle is sent through the network to the remote device. The device that sent the packet then waits and listens for a render packet. If the connections are good and the remote device is online, a practiced return packet will be received. If you lot see issues accessing a website, sending an email, or opening a file on your network file server, the ping tool is used to test and troubleshoot connectivity issue.
These commands shown here are tested on Windows 10 but most will piece of work in other versions of Windows as well.
Table of Content
- Overview
- How to Launch Command Prompt
- Ping Syntax
- Ping Parameters
- Instance Usage
- ping <URL> - Exam Reachability and Latency to a Website
- ping <IP Address> - Exam Reachability and Latency to a Specific IP
- ping -due north -fifty - Ping Using Custom Number of Packets and Parcel Size
- ping -a - Observe Hostname of an IP Accost
- ping <Domain Proper noun> - Discover the IP Accost of a Domain Name/Website
- ping -t - Ping Continuously
- ping 127.0.0.1 - Loopback Address
- Other Usages and Getting Help
- Tips
- Ameliorate Ping Fourth dimension & Troubleshooting
- Ping Responses Explained
- Example of a Practiced Ping Result
- Example Ping Result Showing Remote Device Not Responding
- Redirect Output to Text File
- Add Timestamp to Ping Outcome
- Limitations of Ping Tests
- Recommended Reading
- Summary
Overview
The ping command allows you to ship a signal to another figurer (either on your local network or a computer on the Internet) to determine if it is active or if it can exist reached. This command uses Net Control Message Protocol (ICMP) to send out an ECHO_REQUEST to the target reckoner and waits for an ECHO_REPLY parcel.
The ping command is ane of the primary network troubleshooting tools to test reachability of a remote computer (hence the term "can it be pinged?"). Written by Mike Muuss in 1983, this utility, comprise of about a thousand line of code, was reportedly named "ping" to have it sound like the ping submarine sonar makes.
How ping accomplishes this is by sending a series of small data packet to a device and waiting for a answer from the device to acknowledge (also referred to every bit replies) it received the information. For most Windows calculator, the ping command sends a series of four (4) data packets. Near network devices are configured to automatically mind for and acknowledge receipt of each ping packet sent to them. The ping/reply process typically takes only milliseconds for each data packet. The replies, will allow us know if the device is online and how long information technology took to receive the reply (known as latency).
The ping control reports the following information:
- How many data packets were sent, received, and lost (yous want to see null lost).
- Corporeality of time it took to receive the replies from the remote device - likewise referred to every bit latency. This is expressed in milliseconds, lower is meliorate. Anything lower than 20 milliseconds (ms) is very proficient.
- Time-to-Live (TTL) value that is used to tell the remote device how long to hold/utilise the bundle before it can discard it. The TTL exact value differs based on the operating organization. Maximum value is 255.
- The IP address of the remote device (if it is a URL beingness pinged).
How to Open up Command Prompt
To use this utility, you volition need to launch the Control Prompt window. The 3 common means to launch the Command Prompt window are:
- Search for
cmdusing the built-in Windows search tool. - Right-click on the Start icon and select Command Prompt.
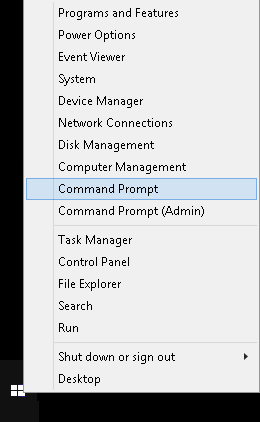
- Press the keyboard combination WinKey + R , and so type
cmdat the Run window that appears.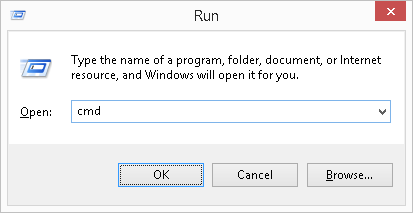
Ping Syntax
ping [/t] [/a] [/northward <Count>] [/l <Size>] [/f] [/I <TTL>] [/v <TOS>] [/r <Count>] [/s <Count>] [{/j <Hostlist> | /k <Hostlist>}] [/due west <timeout>] [/R] [/S <Srcaddr>] [/four] [/6] <TargetName>
Ping Parameters
| Parameter | Clarification |
|---|---|
| -t | Ping the specified host until interrupted. To run into statistics and go along - type Control-Break. To finish - type Control-C. |
| -a | Resolve addresses to hostnames. |
| -north count | Set the number of echo requests to ship. Default is four. |
| -fifty size | Set the length (in bytes) of the data field (send buffer size). The default is 32 bytes. Maximum is 65,527. |
| -f | Set the Don't Fragment flag in packet (IPv4-only) in the IP header fix to 1. The repeat Asking message cannot be fragmented by routers in the path to the destination. This parameter is useful for troubleshooting path Maximum Transmission Unit (PMTU) bug. |
| -i TTL | Set up the Time To Alive value. The default is the default TTL value of the host. The maximum TTL is 255. |
| -five TOS | Type Of Service (IPv4-simply. This setting has been deprecated and has no consequence on the type of service field in the IP Header). |
| -r count | Tape route for count hops (IPv4-merely).Count must be a minimum of 1 and a maximum of 9. |
| -s count | Timestamp for count hops (IPv4-only). Count must be a minimum of ane and a maximum of four. |
| -j host-list | Loose source route forth host-list (IPv4-only). With loose source routing, successive intermediate destinations tin can be separated by 1 or more routers. The maximum number of addresses of names is the host listing is ix (ix). The hostlist is simply a series of IP addresses in dotted decimal annotation (e.k., 192.168.128.8) each separated past spaces. This parameter is only for IPv4 addresses. |
| -k host-listing | Strict source route forth host-list (IPv4-just). With strict source routing, successive intermediate destinations must be directly reachable. The maximum number of addresses of names is the host list is nine (ix). The hostlist is simply a series of IP addresses in dotted decimal note (e.g., 192.168.128.8) each separated by spaces. This parameter is only for IPv4 addresses. |
| -w timeout | Timeout in milliseconds to wait for each reply. |
| -R | Use routing header to test reverse road also (IPv6-only). Per RFC 5095 the utilize of this routing header has been deprecated. Some systems may drop echo requests if this header is used. |
| -S srcaddr | Source accost to use (IPv6-merely). |
| -c compartment | Routing compartment identifier. |
| -p | Ping a Hyper-5 Network Virtualization provider address. |
| -iv | Force tracert to employ IPv4 for the trace. |
| -vi | Force tracert to use IPv6 for the trace. |
| /? | Displays help information. |
Case Usage
There are a diversity of switches (sub commands) bachelor with the ping utility that will configure how it behaves. The examples in this article illustrates mutual ways ping is used.
ping <URL> - Test Reachability and Latency to a Website
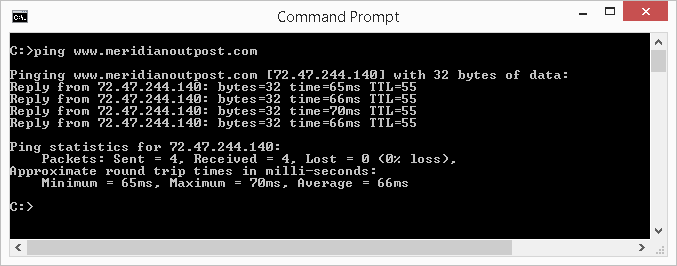
To test network connectivity and latency to a website, such equally www.meridianoutpost.com, type the post-obit in the command window then printing Enter: ping www.meridianoutpost.com
In the example illustration shown beneath, the ping control sent iv data packets to the web server hosting the website www.meridianoutpost.com. There were iv 'pings' sent and four replies received (1 for each of the four 'pings'). Additionally, the ping reports the amount of time it took to receive each of the replies (lower fourth dimension is better) and other useful information. In this case, it shows the boilerplate round trip time (latency) is 66ms and the web server received and replied to all four ping packets.
Lastly, the ping also will report the IP of the website existence pinged, namely 72.47.244.140. Ping will perform a DNS lookup to notice the IP address of the remote device as it is required for any network communication on the Internet.
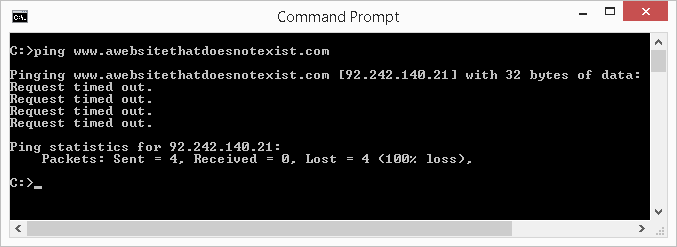
If the website you are pinging is offline, does not exist, or there is no network connectivity to it, ping will response back with time outs or other related messages in its result, as illustrated below.
ping <IP Address> - Test Reachability and Latency to a Specific IP
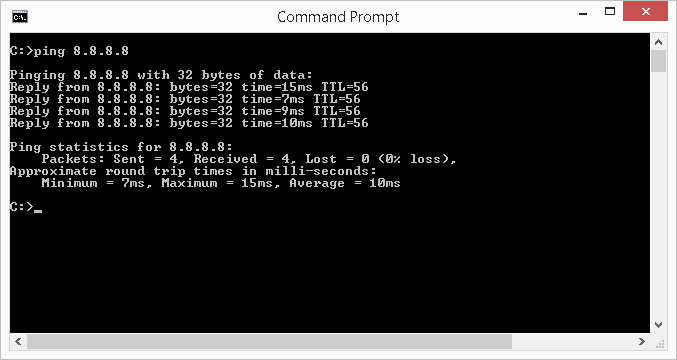
To test network connectivity and latency to a specific IP address, such as 8.8.8.8 (this IP is a Google DNS server), type the post-obit in the command window then press Enter: ping viii.8.8.viii
In the example analogy shown below, the ping command sent four information packets to the server at 8.8.viii.8. There were iv 'pings' sent and four replies received (one for each of the four 'pings'). Additionally, the ping reports the amount of time information technology took to receive each of the replies (lower time is better) and other useful information. In this example, it shows the average round trip time (latency) is 10ms and the server received and replied to all four ping packets.
If the website you are pinging is offline, does not exist, or there is no network connectivity to it, ping will response back with fourth dimension outs or other messages in its result, similar to the those illustrated in the ping <URL> case.
ping -n -50 - Ping Using Custom Number of Packets and Parcel Size
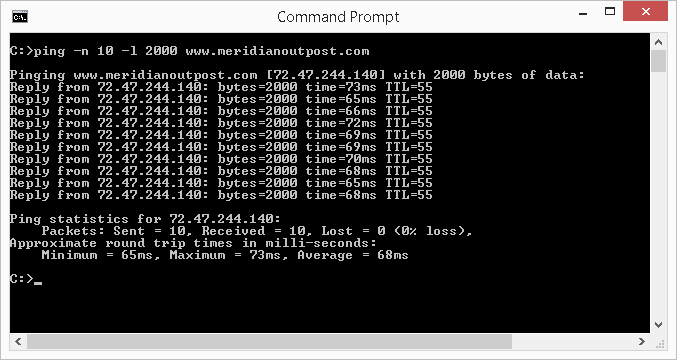
The ping utility allows to you custom how it behaves. Using the -n and -l switches, we tin can define the number of parcel to transport and the size of each parcel, respectively. For example, to send x packets, each sized at 2,000 bytes to the web server hosting the website www.meridianoutpost.com, blazon the following in the command window then press Enter: ping -northward 10 -l 2000 world wide web.meridianoutpost.com
ping -a - Ping to Find Hostname of an IP Address
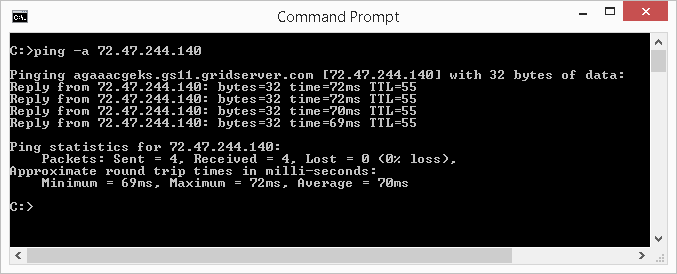
You can utilise the -a switch to have ping written report the hostname of a detail IP accost. For case, the IP address 72.47.244.140 is a spider web server on the Net. To discover out the hostname of this server using ping command, type the post-obit in the command window so press Enter: ping -a 72.47.244.140
In the example illustration shown below, the hostname for the web server with IP address of 72.47.244.140 is agaaacgeks.gs11.gridserver.com.
ping <Domain Proper noun> - Detect the IP Accost of a Domain Proper noun/Website
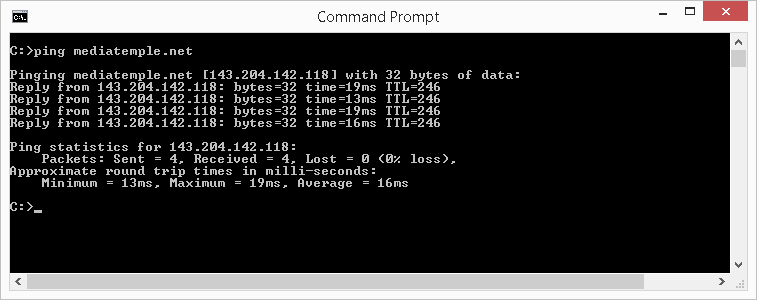
Just similar ping <URL> described previously, yous can look up the IP accost of a website or a domain with the ping utility. For example, to find the IP address to the domain mediatemple.net, type the post-obit in the command window then press Enter: ping mediatemple.net
As the screenshot below shows, the IP for the domain mediatemple.net is 143.204.142.118.
ping -t - Ping Continuously
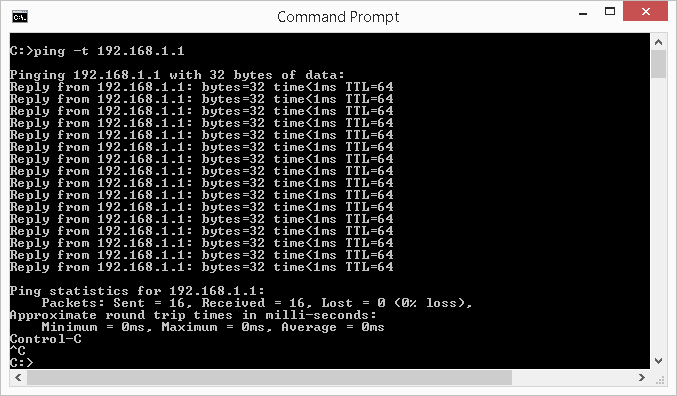
To continuously ping a device, use the -t switch. This will indefinitely ping the remote device until you explicitly stop information technology. The almost common reason for using this switch is to have a existent-time visible indicator to identify was a device comes online or offline. This would typically be in scenarios where administrator are troubleshooting or configuring a organization. By continously pinging the device and looking at the response, i can know when it come up online or offline.
To continuously ping, as an example, the IP accost of 192.168.1.ane, blazon the following in the command window then printing Enter: ping -t 192.168.1.1
You lot can also specify an website URL to continuously ping as well. To terminate the continuous ping, press CTRL+C.
ping 127.0.0.1 - Loopback Address
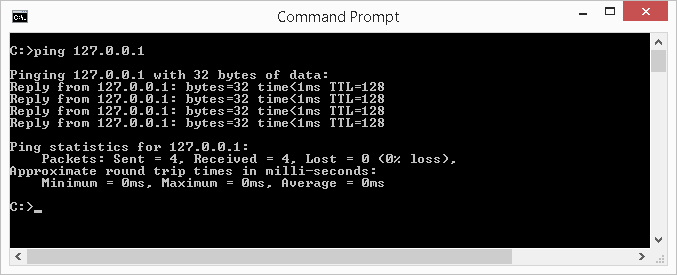
The 127.0.0.1 is a special IP address, chosen a loopback accost. Information technology is a virtual IP accost, in that it cannot be assigned to a device. This IP address is always interrupted to exist 'yourself'. Meaning, if yous ping this IP from your computer, you are pinging your ain computer. If yous are on a file server and you ping this loopback address from that device, yous are pinging that file server.
This loopback address is used to test the device TCP/IP network stack (e.g., network software/driver) of the estimator. If you are experience network connectivity issue on a computer, y'all would kickoff perform ping 127.0.0.ane from that computer first. If ping responses with packet lost, then your connectivity issue is likely on that computer. Yous will need to resolve this showtime before exploring other causes. If the loopback ping reports no package lost, and so your connectivity outcome is not stemming from your computer and you lot can then explore other causes upstream.
Other Usages and Getting Assist
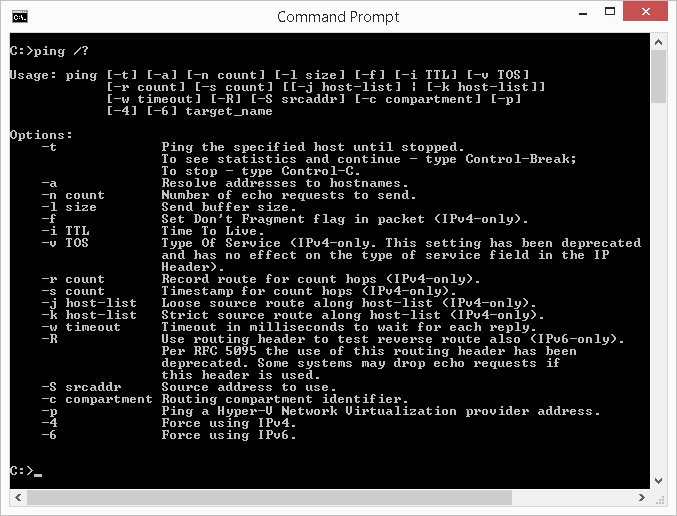
The case usage described in the article shows merely some of the functions bachelor with ping. To get a list of the available switches, type the following in the command window so press Enter: ping /?
Tips
Improve Ping Time & Troubleshooting
- Low ping time is ameliorate than high ping time. For online gaming, a ping time of 100ms or less is good. Ping time of 50ms or less is very skilful.
- High ping time? Try these sugguest to ameliorate to reduce your ping time:
- If you are using a wireless connection, move closer to your router or wireless admission betoken.
- Use a wired connection to your network instead of a wireless connection.
- Close any unnecessary background applications and websites.
- Avoid stream (video, audio) on other computers on your network.
- Reboot your router or modem.
- You tin can check connectivity to diverse devices on the Internet by pinging them (web servers, electronic mail servers, web sites). Slower response times than normal can point network congestion on the network pathway.
- If a ping to a domain name or a web site URL fails, effort pinging its IP address instead. If pinging by IP is successful, this means there is a DNS issue where your computer is unable to resolve the domain or website to an IP address.
- If pinging a host fails, try using the tracert utility to place where the data parcel is failing forth its route.
Ping Responses Explained
- <Destination Host> Unreachable: This ping response indicates a network pathway to the remote device cannot exist found. This can mean a network device betwixt your figurer and the remote device, such as your firewall, is offline or mis-configured.
- No Answer From <Destination Host>: This ping response indicates that the network pathway to the remote device is fine, simply at that place is a trouble with the device itself
- ICMP Host Unreachable From Gateway: This ping response indicates your computer can communication with your local gateway (east.g., your local router) just the gateway itself is unable to reach the remote device. This can mean an upshot with your Internet service provider or Internet service provider-provided device.
- Request Timed Out: This ping response tin can indicate the remote device is offline. However, it is not always the case. A device can be configured to not response to ping requests. Administrators can opt to do this for security reasons every bit they feel that not announcing a device is online tin can minimize their exposure to bad actors on the Net from performing malicious activities (e.g., hacking) against information technology.
- TTL Expired In Transit: This response indicates the amount of time the bundle may live on the network has exceeded the maximum corporeality of "time", more accurately, the number of hops. This can mean that there is a mis-configured router along the network pathway. The TTL (time to live) can exist increased by using the
-iswitch and specifying a value. For example, to specify a TTL of 200 (the maximum value allows is 255) when pinging 8.eight.8.eight, blazon the following in the command window then printing Enter:ping -i 200 eight.8.8.viii - Unknown Host: This response indicates that the IP address or website yous are pinging is not establish on the network or Cyberspace. This can mean either:
- Yous mis-typed your IP or website URL
- A DNS server was not available to resolve the hostname
Example of a Good Ping Upshot
The following is an example of a good ping event. It shows all four examination packets were sent successfully to the remote host. The 4 response packets sent from the remote host is received successfully by the local device (equally indicated by 0% loss). Additionally, the round trip time are not excessively long.
Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=64 Reply from 192.168.1.one: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=64 Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 fourth dimension<1ms TTL=64 Respond from 192.168.1.ane: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=64 Ping statistics for 192.168.1.i: Packets: Sent = 4, Received = four, Lost = 0 (0% loss), Estimate round trip times in milli-seconds: Minimum = 63ms, Maximum = 63ms, Boilerplate = 63ms Example Ping Effect Showing Remote Device Not Responding
The following is an instance ping consequence showing a that four examination packets were sent to the remote device but none were responded to. This tin hateful one of the post-obit probable scenarios:
- At that place a network connectedness event (e.g., network congestion) to the device.
- The device is configured to not response to ping packets (ICMP echo replies). If this is the instance, the device is likely online and operation, despite it not responding to your ping test.
Pinging 192.168.1.222 with 32 bytes of data: Asking timed out. Request timed out. Request timed out. Request timed out. Ping statistics for 192.168.1.222: Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 0, Lost = 4 (100% loss), Example Ping Upshot Showing Remote Device Unreachable
The following is an example ping result showing a problem reaching the remote device. Four test packets were sent and no where received back from the remote host. A ping result like this can meaning ane of the post-obit:
- There is no network route (network path) to the remote device (perhaps due to a firewall or a network router configuration).
- The device is turned off.
- At that place is not device with that IP address.
Pinging 192.168.ane.222 with 32 bytes of data: Destination host unreachable. Destination host unreachable. Destination host unreachable. Destination host unreachable. Ping statistics for 192.168.one.222: Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 0, Lost = 4 (100% loss), Redirect Output to Text File
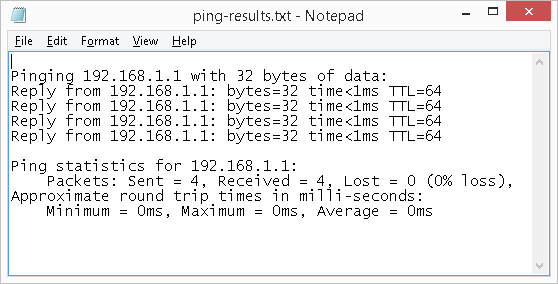
- Instead of displaying the results on the screen, you tin can have the results saved automatically to a text file on your calculator. To do this, merely utilise the ">" symbol followed by the binder path and file proper name of your choice. For example, to redirect the output of ping 192.168.1.1, type the following in the command window and then press Enter:
ping 192.168.1.1 > c:\temp\ping-results.txtThis will create a file named ping-results.txt in the folder path c:\temp that volition have your ping result. You lot can then open this file with any text editor, such as Notepad on a Windows computer, as illustrated beneath.
Add Timestamp to Ping Result
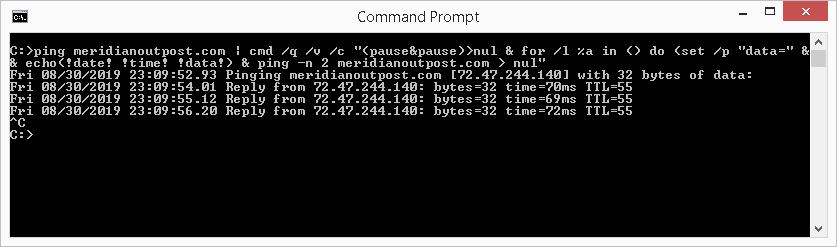
The Windows ping utility does not come with a built-in office report the date and time in its results. However, with a bit of scripting, we can display the appointment and time next to each ping responses. The following script was adult from referencing various posts on StackOverflow. This instance pings the website www.meridianoutpost.com. To come across this script in activity, blazon the following in the command window and then press Enter:
ping meridianoutpost.com | cmd /q /5 /c "(break&pause)>nul & for /50 %a in () practice (set /p "data=" && echo(!date! !time! !data!) & ping -n ii meridianoutpost.com > nul"
You will need to printing CTRL+C to bring back the prompt. Every bit illustrated beneath, this command displays the date and fourth dimension next to each ping response.
Limitations of Ping Tests
Ping accurately measures the network connection between two devices at the time the examination was run. However, because network conditions alter continously, yous should perform a new ping test every fourth dimension you are trouleshooting your network. Test results from yesterday or even the terminal hour may be irrelevant. Additionaly, ping result from one target server tin can vary greatly from the result of some other. Depending on what is it you lot are troubleshooting, yous may need to ping several remote servers to ameliorate understand the problem.
Recommended Reading
Improve confidence and job functioning
Improve productivity and efficiency
Learn more,
earn more than
Life-long
investment
To acquire more than about this topic, we are providing y'all with recommendations to assistance y'all further your noesis. These are our affiliate links to Amazon where you can purchase them and also explore a diverseness of other relevant books.
Summary
Just knowing a device is reachable with a ping does non necessarily mean that the device is fully operating correctly. Existence able to ping a spider web server, for example, only mean the network subsystem is working correctly. However, it does not mean that the Internet Information Services (IIS) on a Windows web server or Apache on a Linux web server application is functioning normal to deliver web page content.
The ping utility is a useful tool for troubleshooting basic network bug. As a helpdesk technician, network administrator, or system administrator, this will undoubtedly be used in conjunction with other advanced tools to effective trouble network issues.
Source: https://www.meridianoutpost.com/resources/articles/command-line/ping.php
Postar um comentário for "5. What Command Do You Use to Determine Whether You Can Reach Another Computer on the Local Network?"